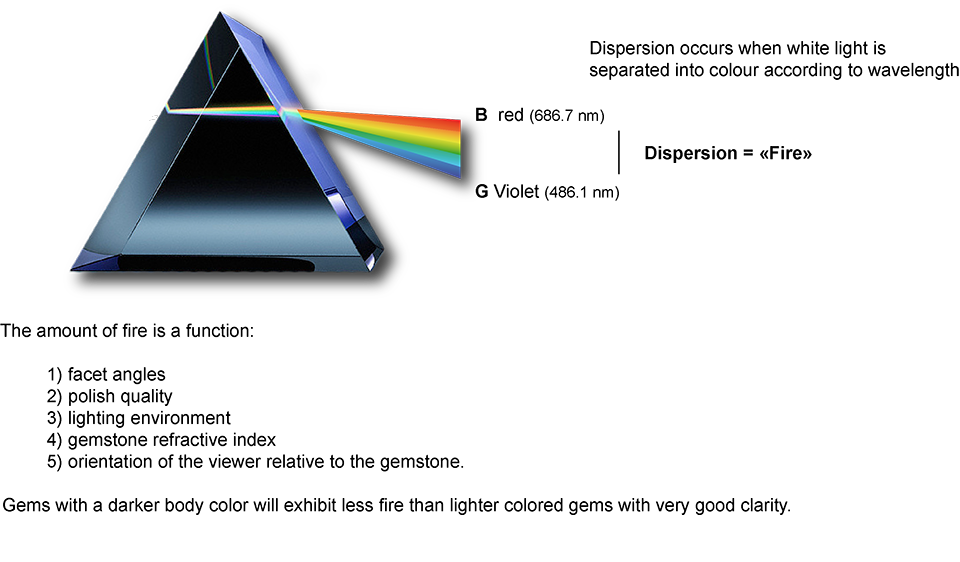

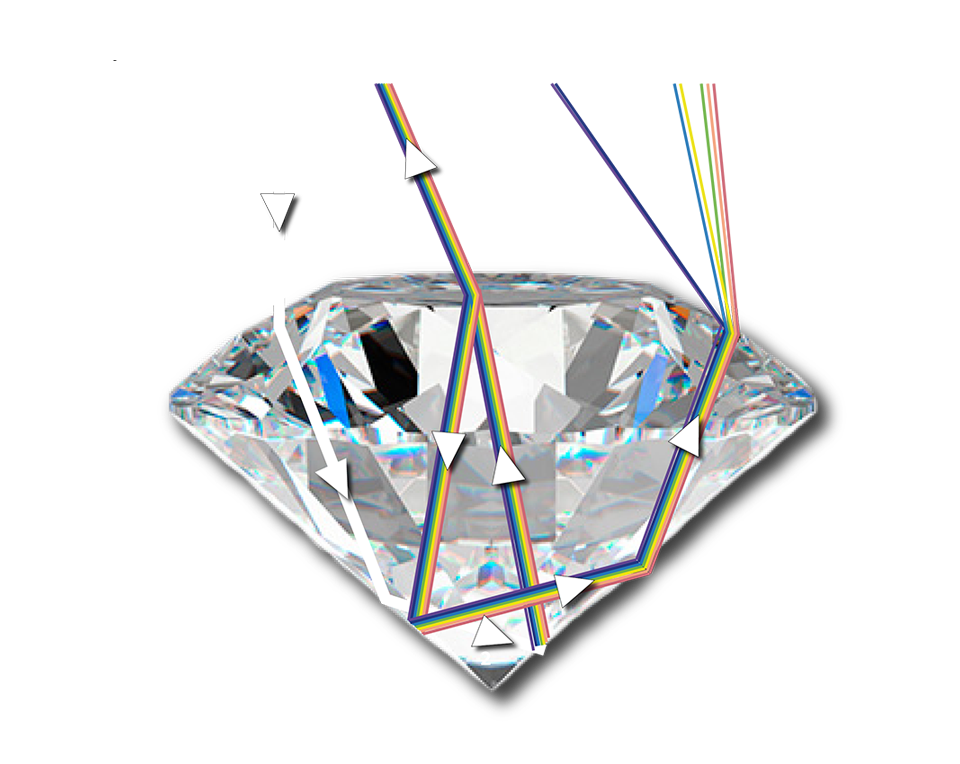









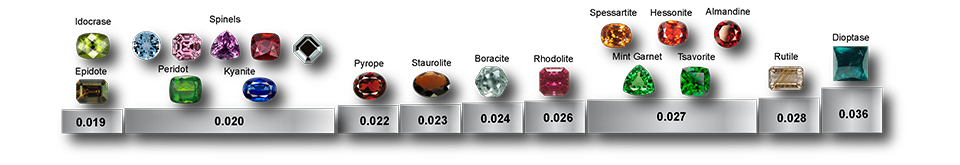
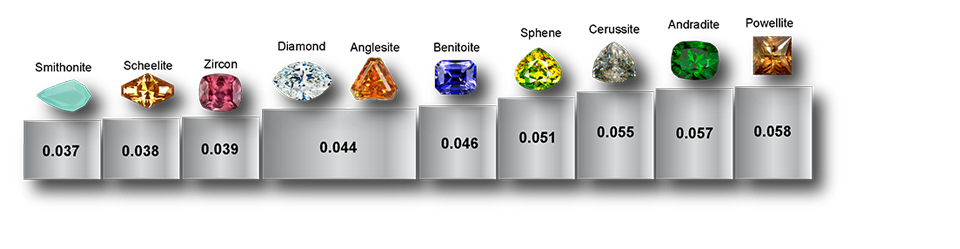
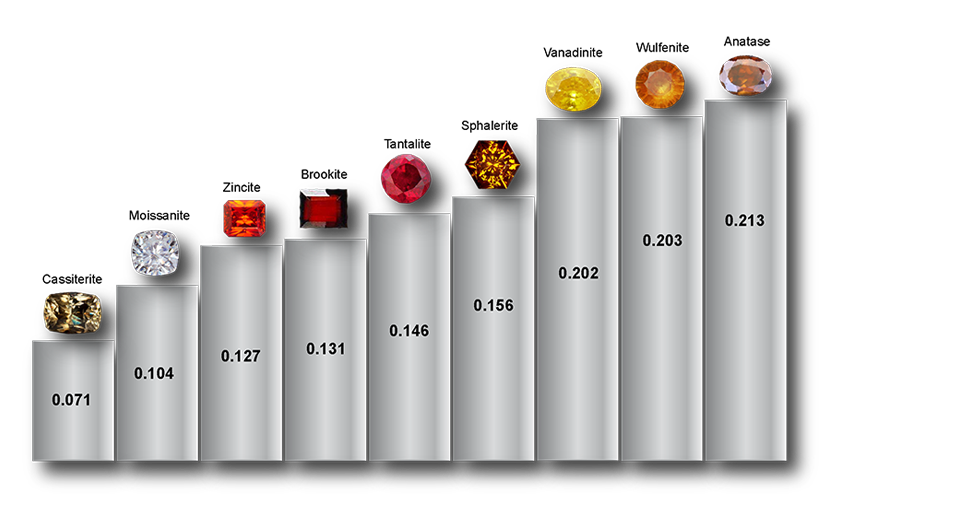
Fracture is the characteristic mark left when a mineral chips or breaks
Luster is the general appearance of its surface in reflected light.


Ex: Muscovite

Basal Cleavage : exhibited on a horizontal plane of the mineral by way of its base. Minerals with basal cleavage can sometimes be "peeled"

Ex: Orthoclase
Prismatic cleavage on some prismatic mine-rals in which a crystal cleaves as thin. verti-cal, prismatic crystals off of the original prism.

Ex: Halite

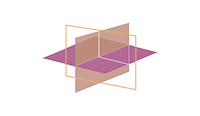
Cubic cleavage exhibited on minerals of the isometric crystal system that are crystallized as cubes. In this method of cleavage, small cubes evenly break off of an existing cube.

Ex: Calcite

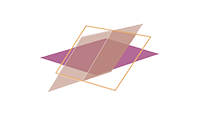
Cleavage exhibited on a horizontal plane of the mineral by way of its base. Minerals with basal cleavage can sometimes be "peeled"

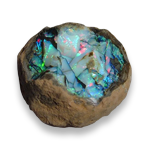

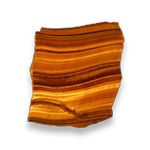

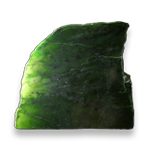











Smooth crystal e'ge not very visible rough surface is dominant.










Smooth crystal e'ge not very visible rough surface is dominant.




Smooth crystal e'ge not very visible rough surface is dominant.












Smooth crystal e'ge not very visible rough surface is dominant.






Smooth crystal e'ge not very visible rough surface is dominant.